INCOME STATEMENT
Definition
The Income Statement, also known as the Profit and Loss Statement (P&L) or Statement of Earnings, is a financial report that shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific accounting period—typically quarterly or annually.
It answers the question: "How much did the company earn over a given time?"
Origins
The income statement has evolved from double-entry bookkeeping systems developed in Renaissance Italy. In the 20th century, its format was standardized through GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) to ensure consistency and comparability in financial reporting.

Usage
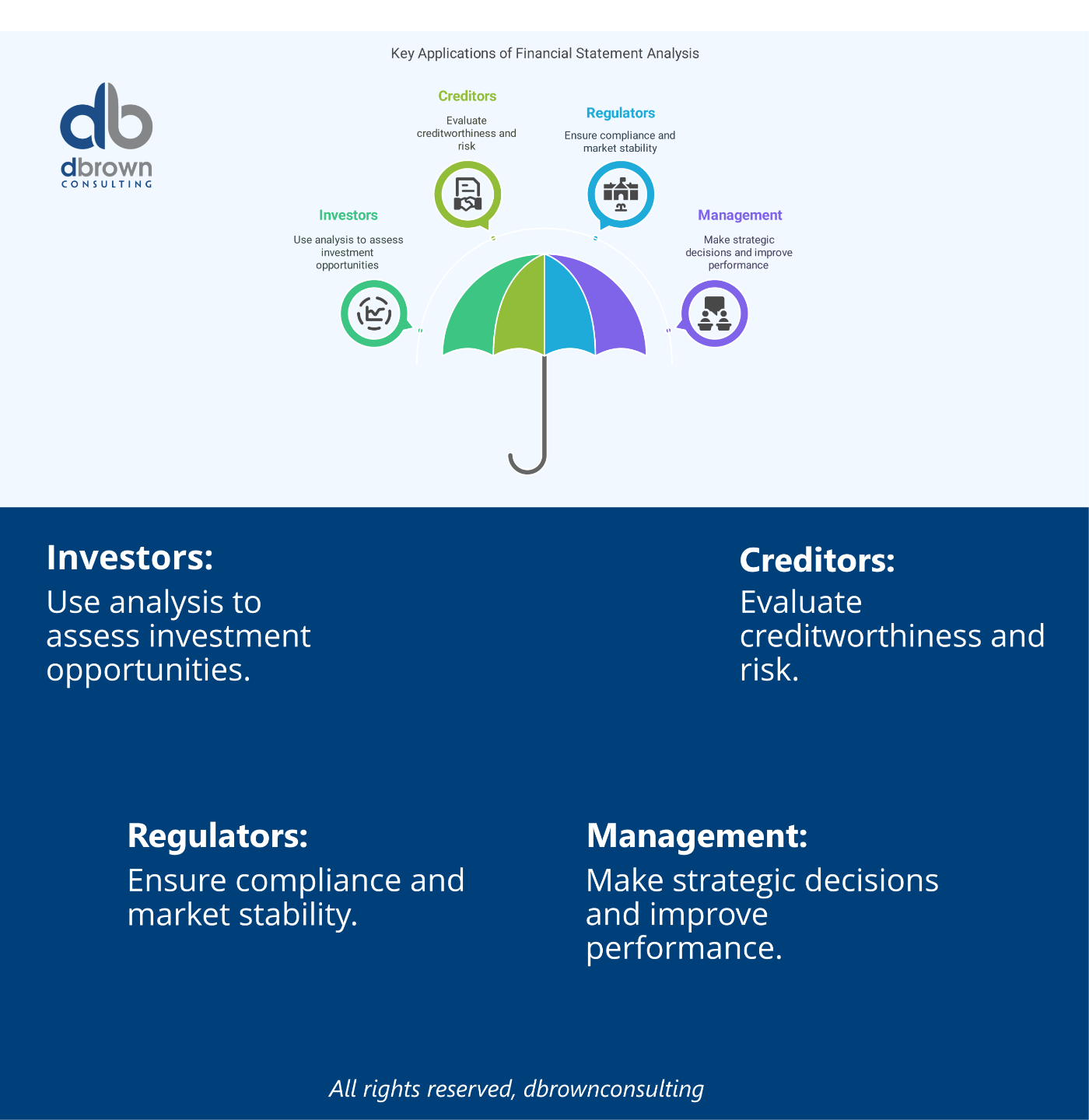
Industry Applications:
-
Financial Reporting – Required by regulators (SEC, FASB, IFRS).
-
Investment Analysis – Assess profitability, growth, and valuation.
-
Credit Risk Evaluation – Determine borrower’s income sufficiency.
-
M&A Due Diligence – Analyze historical performance and synergies.
-
Strategic Planning – Inform pricing, cost control, and budgeting.
-
KPI Tracking – Metrics like EBITDA, gross margin, and net margin.
How Income Statement works
The income statement shows how revenues are transformed into net income through various layers of expenses.
Key Line Items (Top to Bottom Structure):
-
Revenue (Sales)
-
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
-
Gross Profit
-
Operating Expenses (SG&A, R&D)
-
Operating Income (EBIT)
-
Non-Operating Items (interest, investment income)
-
Earnings Before Taxes (EBT)
-
Income Tax Expense
-
Net Income (or Net Loss)
Optional Additions:
-
EBITDA – Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization.
-
Earnings per Share (EPS) – For publicly traded companies.
Key Takeaways
-
Shows profitability over time, not cash flow.
-
Used by stakeholders to assess company performance.
-
Must align with accounting standards (accrual basis).
-
Accompanied by footnotes explaining policies and non-recurring items.
-
Works in tandem with the Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement.
Types of Income Statements
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Single-Step | Combines all revenues and expenses for one-step net income calculation. |
| Multi-Step | Separates operating vs. non-operating income and highlights gross/operating profit. |
| Pro Forma Income Statement | Adjusted for non-recurring items, used for forecasting or M&A modeling. |
| Segment Income Statement | Breaks down by business unit, region, or product line. |
| Common-Size Statement | All items expressed as a % of total revenue—useful for benchmarking. |
Income Statement & Financial Modeling
Central to:
-
Three-Statement Financial Models:
-
Feeds into retained earnings on balance sheet and cash flow from operations.
-
-
Valuation Models:
-
DCF: Earnings → FCFF or FCFE
-
Comps: P/E, EV/EBITDA based on income statement inputs.
-
-
Budgeting & Forecasting:
-
Project sales, margins, and cost trajectories over time.
-
-
Scenario Analysis:
-
Flex revenue, cost, or tax assumptions for best/worst cases.
-
Nuances & Complexities
-
Revenue Recognition: Governed by standards (ASC 606, IFRS 15); may not match cash inflows.
-
Non-Recurring Items: Must be adjusted for core earnings analysis.
-
Depreciation & Amortization: Non-cash but affects operating income.
-
Tax Strategy: Deferred taxes, loss carryforwards impact bottom line.
-
IFRS vs. GAAP Presentation: Different formats and terminologies may apply.
Mathematical Formulas
1. Gross Profit:
2. Operating Income (EBIT):
3. Net Income:
4. Earnings per Share (EPS):
Master Financial Modeling with the FMA
Change your career today by earning a Globally Recognized Accreditation
Develop real-world financial modeling skills, gain industry-recognized expertise, stand out and start earning more by gaining the Advanced Financial Modeler (AFM) designation from the Financial Modeling Institute.
Our expert-led online cohort based program covers everything you need to become a world class financial modeling pro and advance your career in finance.
Related Terms
-
Revenue
-
COGS
-
EBITDA
-
Net Income
-
Retained Earnings
-
Accrual Accounting
-
EPS
-
Pro Forma Statements
-
Revenue: $383B
-
Gross Profit: $170B
-
Net Income: $97B
-
Gross Margin: ~44%
References & Sources
-
IFRS IAS 1 – Presentation of Financial Statements
-
SEC 10-K Filings – Income Statements of Public Companies
Unlock the Language of Finance!
Elevate your financial acumen with DBrown Consulting’s exclusive newsletter. We break down complex finance terms into clear, actionable insights—empowering you to make smarter decisions in today’s markets.
Subscribe Today & Make Financial Jargon Simple!
We won't send spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

